Why Green Hydrogen Is a Sustainable Fuel Source

Hydrogen: A Truly Sustainable Alternative Fuel
Chuck Hayes, Global Technical Lead, Swagelok
The world continues to develop alternatives to fossil fuels. Sustainability is the primary motivator. Reducing and outright eliminating carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from a wide variety of applications is an increasingly important goal.
When it comes to any potential alternative fuel, it’s important to ask: Is it truly sustainable?
Critics have asked this question of hydrogen, one of the more promising alternative fuels that continues to gain traction in many applications. The answer is “Yes, hydrogen can be a sustainable alternative fuel.” And in this final installment of our series debunking the most common myths about hydrogen, we’ll explore the different ways hydrogen is produced and why hydrogen represents a truly sustainable alternative fuel option.
Types of Hydrogen Fuel and Production Methods
It is important to note that hydrogen’s sustainability depends on how it’s made. It takes energy to produce hydrogen, and the source of that energy and the production method used determine how sustainable hydrogen truly is. To understand how “clean” hydrogen production is, it’s important to understand the different colors by which it’s classified:
 Gray Hydrogen
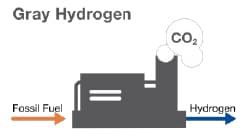
Gray Hydrogen
Gray hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels, resulting in emissions of a reduced amount of carbon dioxide compared to direct burning of fossil fuels. Today, gray hydrogen is the cheapest to generate and represents the majority of the world’s hydrogen production.
Two production methods are primarily used to create gray hydrogen: steam methane reforming and coal gasification. Both of these processes release CO2 into the atmosphere, making gray hydrogen the least sustainably produced of the types we’ll cover here.
 Blue Hydrogen
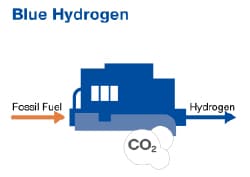
Blue Hydrogen
Similarly to gray hydrogen, blue hydrogen forms via steam methane reforming and coal gasification. However, in the blue hydrogen production process, CO2 emissions are captured and stored instead of being released into the atmosphere.
This carbon capture results in the classification of blue hydrogen as a low-carbon fuel and a more sustainable option than gray hydrogen. However, the carbon capture process adds cost to the production cycle, slightly elevating the price of the fuel.
 Green Hydrogen
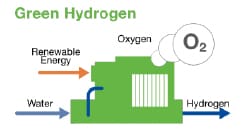
Green Hydrogen
Green hydrogen is produced via electrolysis, a process that splits water into oxygen and hydrogen. To be classified as green, the electrolysis process must use renewable electricity generated from wind or solar power. These measures ensure green hydrogen is a true zero-emissions fuel source. The use of these clean alternatives adds to the cost of production.
Why the Cost of Hydrogen Is Coming Down
While blue and green hydrogen are more expensive to produce than gray hydrogen and traditional fossil fuels, the cost for consumers will only drop over time. This will happen for a few reasons.
First, major oil producers are reducing production levels that have created unsustainably low prices. They are likewise making decarbonization commitments over the long term. These measures will likely raise gasoline and diesel prices for consumers who drive internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
Meanwhile, experts anticipate green hydrogen fuel will be cost-competitive with traditional fuel sources within 10 years. This is in part due to the falling cost of solar, wind, and water power generation, which will further influence hydrogen pricing. Finally, as governments across the globe enact more stringent carbon dioxide emissions standards, expect more government subsidies to incentivize clean energy growth.
The Bottom Line
Hydrogen can be produced sustainably and is one of the most environmentally friendly alternatives to fossil fuels currently on the market. And despite the varying sustainability profiles of different types of hydrogen, even gray and blue hydrogen minimize CO2 emissions at their point of use. Meanwhile, significant investment in green hydrogen is only increasing throughout the world, with industry stakeholders working to find more ways to improve production efficiencies and drive down prices for end users.
Interested in learning more about the clean energy economy? At Swagelok, we’re hard at work to deliver reliable fluid system solutions for companies on the leading edge of hydrogen and other alternative fuels, and we’re committed to sharing our knowledge. Explore Swagelok Reference Point for more critical considerations about the clean energy industry.
Related Articles

Is Hydrogen a Safe Fuel Source?
Hydrogen has the potential to be a revolutionary clean energy source, but some common myths abound about the fuel’s safety. Get the facts about hydrogen as we explore why it’s a safer fuel source than conventional options.

FAQs: How to Avoid Hydrogen Embrittlement
Selecting the right materials for hydrogen-handling applications is critical to the long-term viability of hydrogen as a fuel source. Learn how to select the right materials and prevent hydrogen embrittlement.

Optimize Your Electrolyzers With Fluid System Support
The hydrogen electrolysis process depends on reliable inflow and outflow fluid systems. Learn how you can control costs, enhance safety, and maximize productivity with the right fluid system support.



